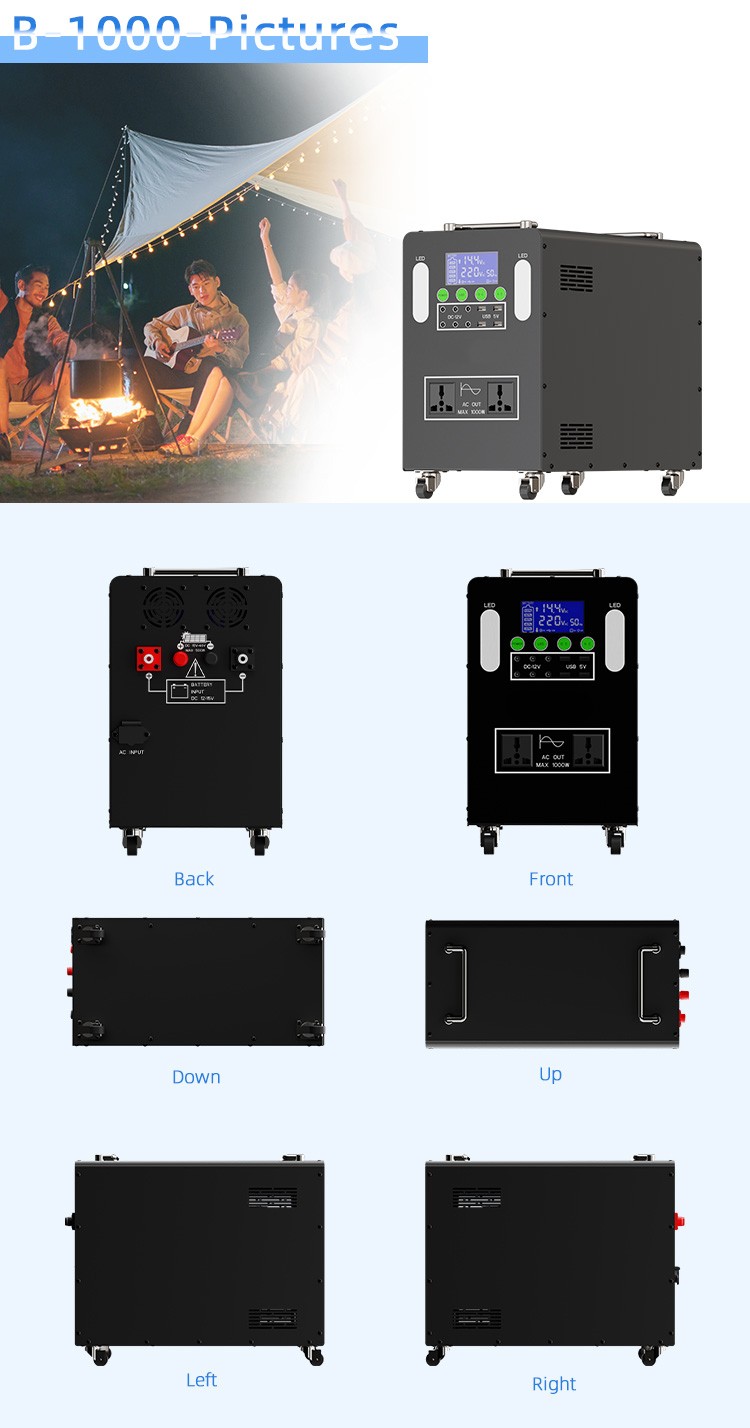
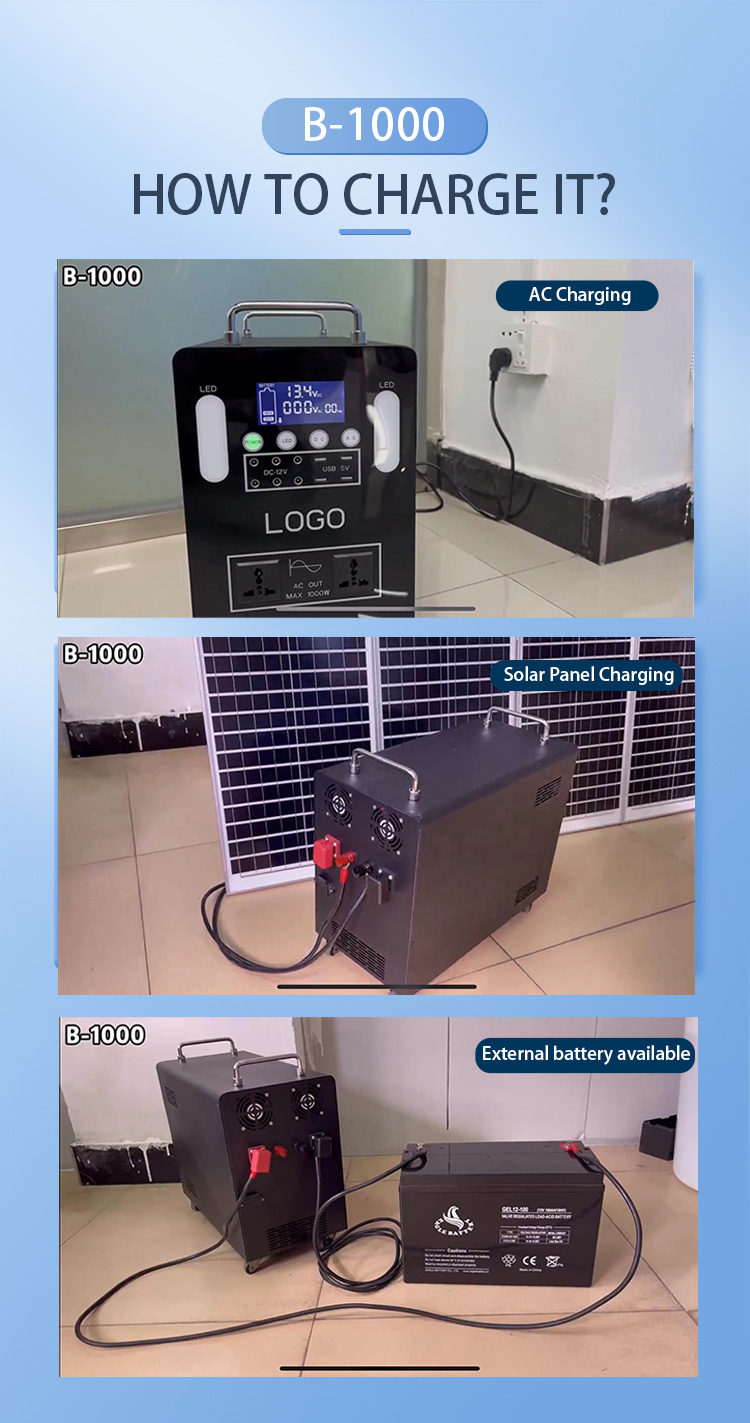
Principles of converting lead-acid batteries to lithium batteries in portable power stations
Jun. 23, 2025
I. Differences in battery characteristics and adaptation principles
Energy density improvement
The energy density of lithium batteries (such as lithium iron phosphate and ternary lithium) is much higher than that of lead-acid batteries, and more electrical energy can be stored at the same volume or mass. For example, the energy density of lithium batteries can reach 200-300Wh/kg, while that of lead-acid batteries is only about 30-50Wh/kg. This means that the battery life of the equipment after modification is significantly extended, or the volume and weight are greatly reduced.
Voltage and capacity matching
· Voltage matching: The original system rated voltage must be kept consistent (such as 12V, 48V, etc.), but the voltage of lithium battery cells is different (such as lithium iron phosphate 3.2V/cell, lead acid 2V/cell), and the target voltage of 25 must be reached by series connection.
· Capacity matching: The total capacity of the lithium battery is calculated based on the original lead-acid battery capacity, and the difference in discharge rate (C rate) must be considered. For example, a 1C discharge of a lead-acid battery may correspond to a 0.5C discharge of a lithium battery.
Adjustment of charging and discharging characteristics
The charging cut-off voltage of lithium batteries is stricter (such as 3.65V/cell for lithium iron phosphate), and a constant current and constant voltage charging stage is required, while lead-acid batteries have a wider adaptability. It is necessary to replace a dedicated charger or adjust the charging curve to avoid overcharging and overdischarging.
2. System architecture transformation and core components
Battery management system (BMS)
Lithium batteries must be equipped with BMS to monitor voltage, current, and temperature to prevent overcharging, overdischarging, short circuit, and thermal runaway. BMS also needs to achieve battery balancing (such as passive balancing or active balancing) to ensure the consistency of multiple strings of batteries.
Battery pack structure design
Series and parallel rules: Lithium batteries cannot be connected in series and parallel at will, and must be combined according to specific rules. For example, communication base station lithium battery packs are usually only connected in parallel, not in series, to avoid consistency problems.
Modular assembly: The single cells need to be connected in series (voltage increase) and parallel (capacity expansion) to form a battery pack, and safety protection components (such as fuses and temperature sensors) must be added.
Optimization of charging and discharging circuits
Replace the original lead-acid charger with a lithium battery charger to support more precise voltage and current control.
In UPS and other equipment, the inverter parameters need to be adjusted to match the charging and discharging characteristics of lithium batteries.