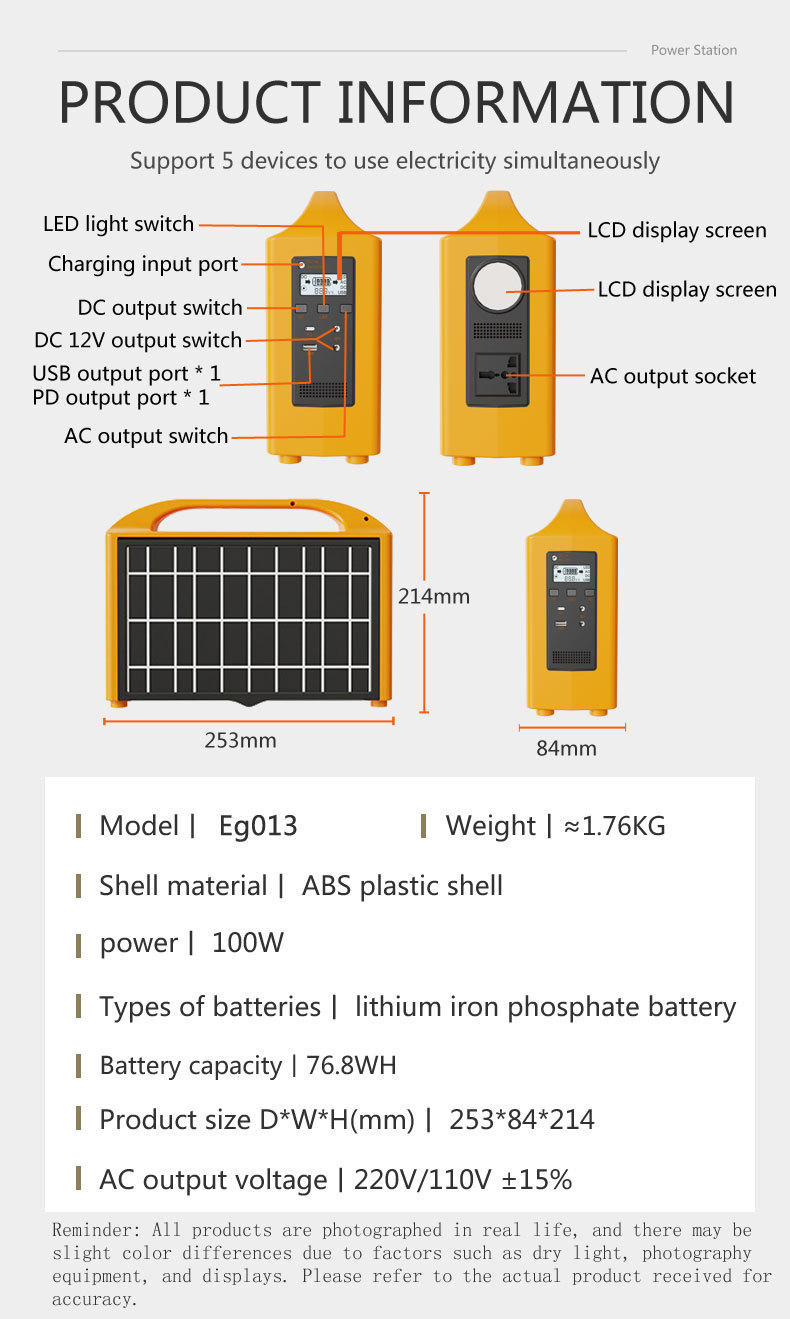
What are the safety protection mechanisms of portable power stations?
Jun. 21, 2025
1. Core protection functions of battery management system (BMS)
The battery management system (BMS) is the "smart brain" of the energy storage power supply. It monitors the battery status in real time and executes protection strategies to avoid safety risks caused by abnormal conditions such as overcharging, over-discharging, and overcurrent.
1. Overcharge protection
Protection mechanism:
· Cut off the charging circuit and stop charging;
· Some high-end products support the "trickle charging" mode, which resumes low-current charging after the voltage drops back to the safe range to avoid overcharge damage.
· Application scenario: Prevent the risk of battery expansion and fire caused by charger failure or user forgetting to unplug.
2. Over-discharge protection
· Protection mechanism:
· Cut off the discharge circuit and force output to stop;
· Keep 5%-10% of the power as the "protection power" to avoid permanent capacity decay ("starvation") caused by deep discharge of the battery.
· Application scenario: Avoid long-term driving of high-power equipment or forgetting to turn off the load, which may cause the battery to be scrapped.
3. Overcurrent protection
·Protection mechanism:
·Cut off the circuit through MOS tube or fuse;
·Some BMS support "recoverable protection", and automatically restore power supply after the current falls back to the safe range.
·Application scenario: Prevent battery overheating or line burning caused by short circuit and load overload (such as starting multiple high-power devices at the same time).
4. Overheat protection
·Protection mechanism:
·Reduce the charge/discharge power (such as limiting the current to 50% of the rated value);
·Start active cooling (fan running at full speed);
·Cut off the circuit when the temperature continues to rise.
·Application scenario: Prevent thermal runaway of the battery when working in a high temperature environment, running at full load for a long time or when the cooling system fails.
5. Low temperature protection
·Protection mechanism:
·Charging is prohibited (to avoid low temperature charging causing lithium dendrite growth, piercing the diaphragm and causing short circuit);
·Allow small current discharge (such as only supporting USB interface power supply). Some high-end products have built-in heating films, which automatically heat up to above 5℃ and resume charging.
·Application scenario: outdoor use in winter or in cold storage environment to ensure battery safety and life.
2. Circuit system safety protection
In addition to the battery itself, the input/output circuit of the energy storage power supply also requires multiple protections to ensure the stability of the power conversion process.
1. Overload protection
·Protection mechanism:
·The inverter immediately turns off the AC output, and the BMS cuts off the discharge circuit;
·Requires manual reset or power off and restart to recover (some products support automatic reset).
2. Short circuit protection
·Causes direct conduction of positive and negative poles.
·Protection mechanism:
·Nanosecond fast response, instantaneous current cutoff through hardware circuits (such as comparator + MOS tube);
Some high-end products are equipped with "short circuit protection"